Content
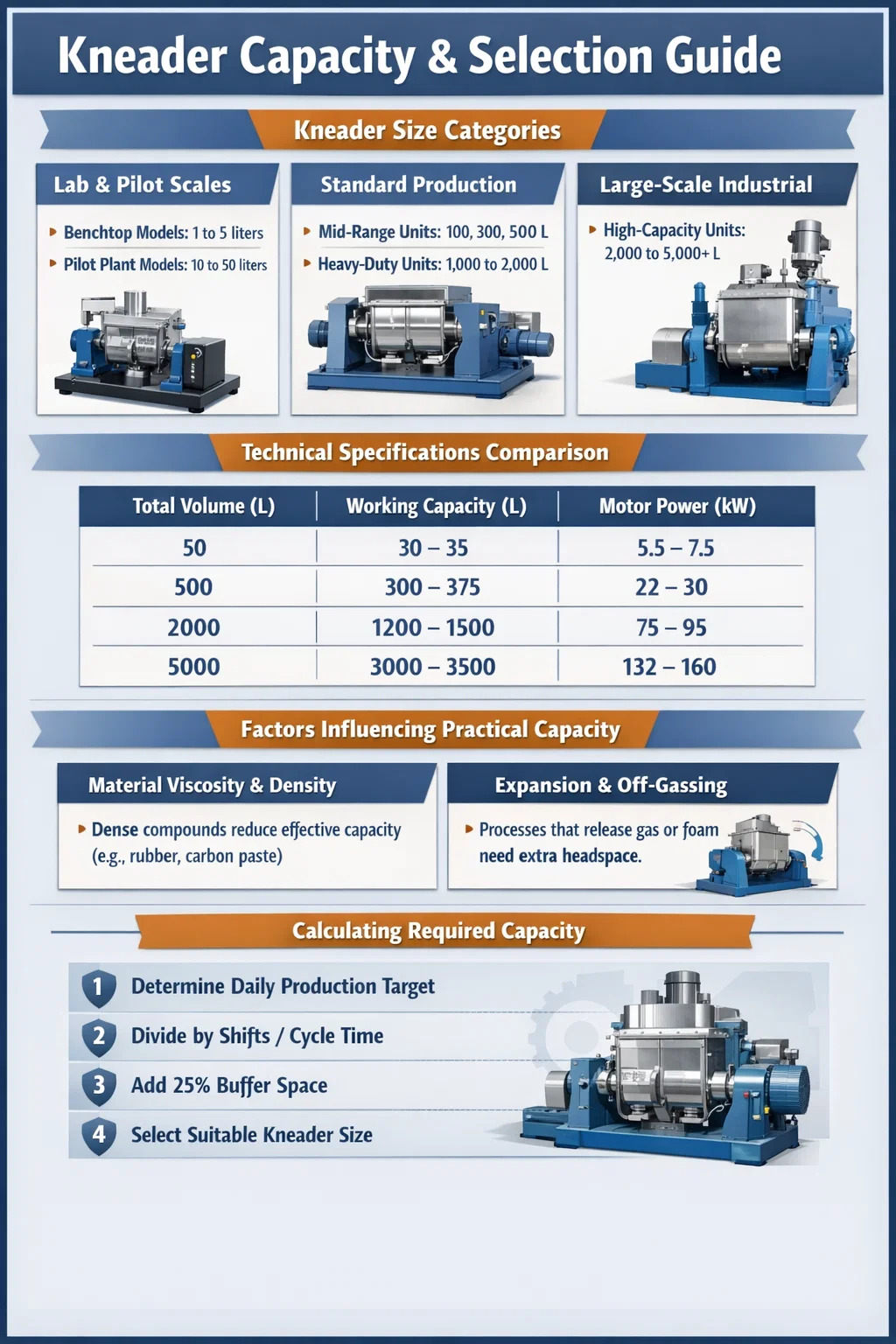
Direct Answer: Typical Kneader Capacity Ranges
The capacity of a kneader varies significantly depending on its intended use, ranging from 1 liter for laboratory research to over 5,000 liters for large-scale industrial manufacturing. In most standard industrial applications, the "working capacity" is generally considered to be 60% to 75% of the total volume of the mixing bowl to allow for efficient folding and shearing of the material.
Categorizing Kneader Sizes by Application
When selecting a kneading machine, it is crucial to match the volume to the production stage. Machines are typically categorized into three main tiers based on their total volume:
Laboratory and Pilot Scales
Small-scale kneaders are used for R&D and recipe testing. These units allow chemists to test high-viscosity formulations like specialized adhesives or pharmaceutical pastes without wasting expensive raw materials.
- Benchtop Models: 1 to 5 liters.
- Pilot Plant Models: 10 to 50 liters.
Standard Industrial Production
For mid-sized manufacturing, such as silicone rubber production or ink mixing, the sigma blade kneader is the industry workhorse. These machines provide enough throughput for commercial viability while remaining manageable in terms of factory footprint.
- Mid-Range Units: 100, 300, and 500 liters.
- Heavy-Duty Units: 1,000 to 2,000 liters.
Technical Specifications Comparison
Understanding the relationship between total volume and motor power is essential, as higher capacity kneading equipment requires significantly more torque to process thick materials.
| Total Volume (L) | Working Capacity (L) | Typical Motor Power (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| 50 | 30 - 35 | 5.5 - 7.5 |
| 500 | 300 - 375 | 22 - 30 |
| 2000 | 1200 - 1500 | 75 - 95 |
| 5000 | 3000 - 3500 | 132 - 160 |
Factors Influencing Practical Capacity
The effective capacity of a rubber kneader or chemical mixer isn't just a matter of the tank size. Several physical factors determine how much material you can actually process per batch:
Material Viscosity and Density
Extremely dense materials, such as carbon paste or heavy rubber compounds, exert immense pressure on the kneader blades. In these cases, the working capacity might be reduced to 50% of the total volume to prevent motor burnout or shaft breakage.
Expansion and Off-Gassing
If the process involves a chemical reaction that releases gases or causes the mixture to foam, a larger "headspace" is required. For example, in vacuum kneaders, leaving at least 30% free space is vital to ensure that the vacuum pump doesn't pull raw material into the filtration system.
How to Calculate Required Capacity
To determine the right kneader size for your facility, follow these practical steps:
- Identify your daily production target in kilograms.
- Divide the daily target by the number of shifts or hours available.
- Account for cycle time (typically 30 to 90 minutes for high-viscosity mixing).
- Select a total capacity that allows for a buffer of 25% empty space above the final mixed volume.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى

