Content
A kneader, also known as a mixer or dough mixer, is an industrial device primarily used for powerfully mixing, kneading, and stirring materials to achieve a uniform, plastic state. You can imagine it as a super-powerful mixing bowl, but instead of everyday ingredients, it handles various viscous, semi-solid, or high-viscosity materials that require high-intensity mixing in industrial production.
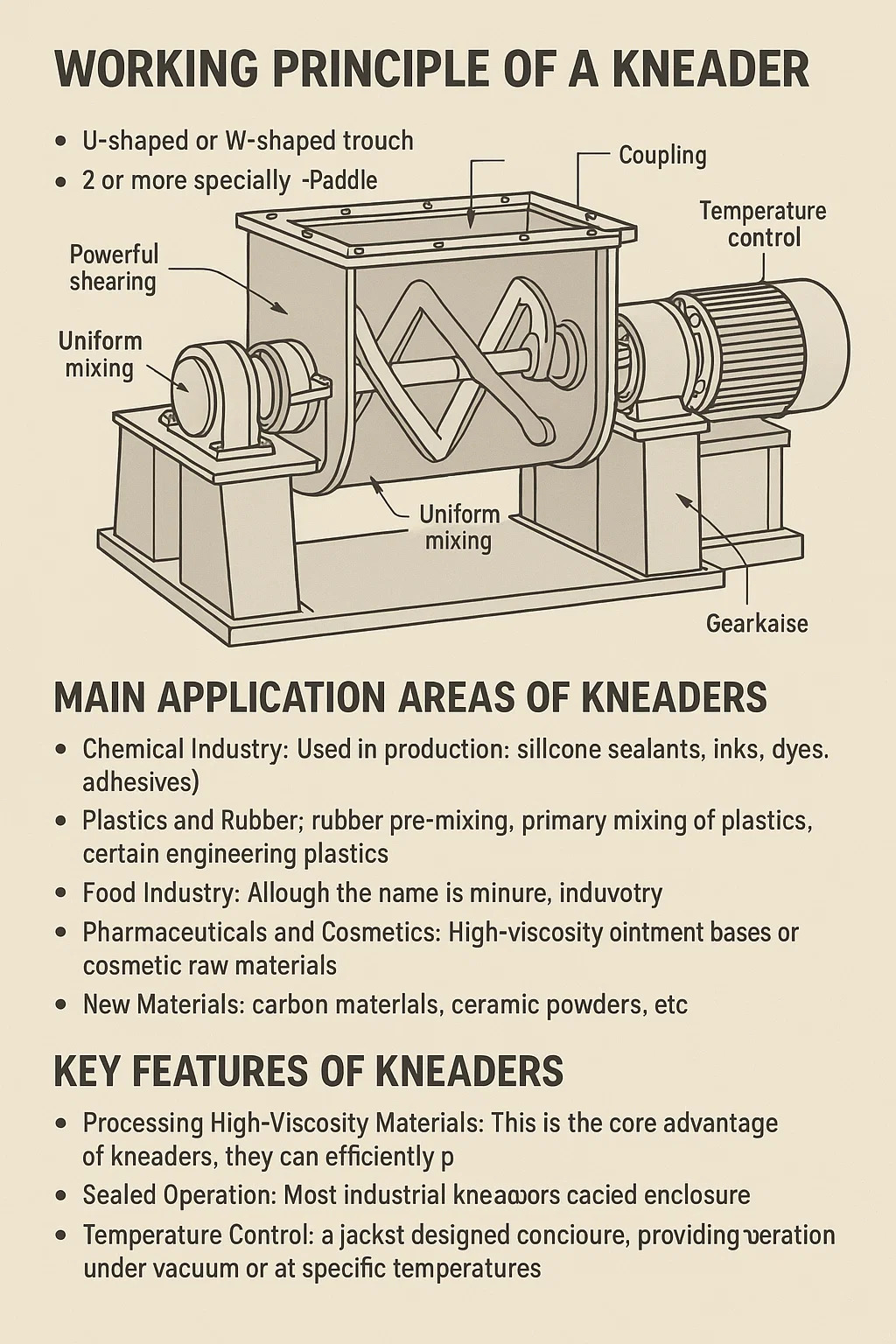
■ Working Principle of a Kneader
A kneader typically consists of a U-shaped or W-shaped trough and two or more specially shaped mixing paddles (most commonly Z-shaped blades).
▸ Paddle Movement: The mixing paddles inside the trough rotate in opposite directions at different speeds (i.e., differential speed).
▸ Powerful Shearing: This differential counter-rotation subjects the material to powerful shearing, compression, folding, and tearing forces between the paddles and between the paddles and the trough wall.
▸ Uniform Mixing: Under these forces, the originally non-uniform material is repeatedly and forcefully "kneaded" together, achieving thorough mixing, dispersion, and homogenization, ultimately resulting in a uniformly textured mixture.
■ Main Application Areas of Kneaders
Kneaders are indispensable key equipment in many heavy and light industries, excelling at processing high-viscosity materials that are difficult for ordinary mixers to handle:
▸ Chemical Industry: Used in the production of silicone sealants, inks, dyes, adhesives (glues), etc.
▸ Plastics and Rubber: Used for rubber pre-mixing, primary mixing of plastics, and processing of certain engineering plastics.
▸ Food Industry: Although the name is similar, industrial kneaders and kitchen "dough mixers" have similar principles, used for large-scale production of dough, chewing gum base, etc.
▸ Pharmaceuticals and Cosmetics: Used for processing certain high-viscosity ointment bases or cosmetic raw materials.
▸ New Materials: Used for high-difficulty mixing of carbon materials, ceramic powders, etc.
■ Key Features of Kneaders
▸ Processing High-Viscosity Materials: This is the core advantage of kneaders; they can effectively process very high-viscosity, non-flowing materials.
▸ Sealed Operation: Most industrial kneaders are designed with a sealed enclosure, allowing for operation under vacuum or at specific temperatures, preventing material contamination or solvent evaporation.
▸ Temperature Control: The mixing chamber is typically designed with a jacket that allows for the circulation of steam or cooling water, enabling heating or cooling of the materials during the kneading process to ensure that the reaction or mixing takes place at the ideal temperature.

 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى

